The 4 Major Areas of Healthcare Impact of the Big Beautiful Bill Act
After reading this article, you will be able to realize the immediate and long-term negative clinical and financial complexities of the new law on healthcare.
SUMMARY:
Major rollbacks to Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act subsidies are the main targets of the Bill
Millions will lose insurance coverage
A financial strain will be placed on all states, hospitals, and providers as they lose Medicaid revenue
The full impact will not be known for years
COMMON PAIN POINTS
Significant reductions in reimbursement
Millions of uninsured patients needing uncompensated care
Limiting health services, care delays, longer wait times (especially in ED)
REVIEW
The Bill decreases Medicaid payments to:
States by $863 Billion over 10 years
Hospitals by $321 Billion over 10 years
Physicians by $81 billion
Prescription payments by $191 Billion
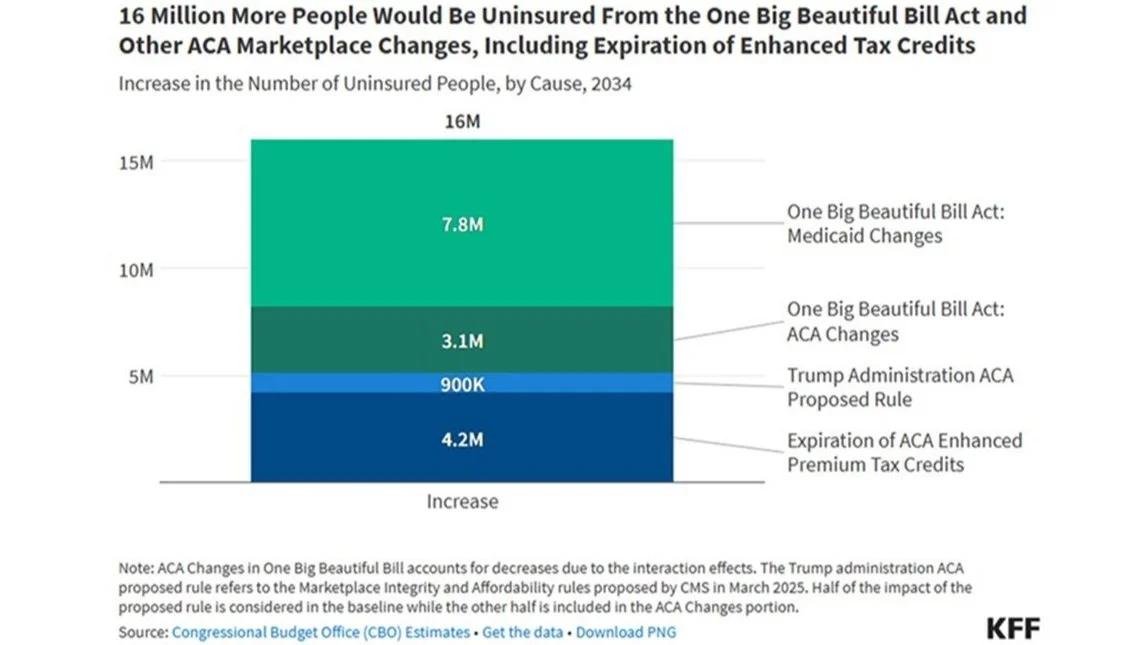
The changes will result in an estimated loss of insurance in 11.8 to 16 million individuals
The Bill will shift the cost of care from the federal government to providers and local governments.
Translates into more uninsured patients, more uncompensated care, and more medical debt.
The Congressional Budget Office estimates the Bill will add $3.3 trillion to the national deficit.
Medicaid funding changes are not scheduled to take effect until 2028.
Work requirements are to begin no later than December 2026.
Two rules are delayed until 2035:
Reduced barriers to enrollment in the Medicare Savings Program (MSPs), which help low-income Medicare participants with Medicare premiums
Streamline application and enrollment in Medicaid
The Work Requirement
Accelerated into 2026
Medicaid participants aged 19-64, who are childless, without disabilities, and parents of children over age 14, must work, volunteer, or attend school at least 80 hours per month, unless they qualify for exemption.
The impact of the Bill:
Estimates range from 11.8 to 16 million people will lose health insurance by 2034
Severely restricts how states pay for their share of Medicaid costs
Creates several new bureaucratic hurdles
Rural hospitals are heavily dependent on Medicaid revenue.
Estimated rural hospitals will lose $50.4 billion in 10 years and 1.8 million rural residents will lose coverage.
Savvy Approaches
Doing nothing will doom you to failure
Operational changes are not sufficient to solve these problems.
ED Wait times and overcrowding will worsen
Rural hospitals with already thin margins will be under greater financial pressure
Safety net hospitals will provide an increased level of uncompensated care
Larger strategies are needed to address the uncompensated care provided.
Requires a multifaceted approach
Innovation and analytics
Goals are to:
Improved care delivery mechanisms
Control expenses
Increase efficiency - Lower cost sites of care
Maximize profitable service lines
Decreased prices of basic services
Revenue cycle management – identify underpayments
Since costs are being shifted to states, their options are:
Raise taxes
Eliminate other services
Make deeper cuts into the state run Medicare program
CONCLUSIONS:
Elimination of the Affordable Care Act premium subsidies with financial loss to providers and loss of insurance coverage to 5 million individuals
Up to 16 million individuals will lose insurance coverage, particularly low-income individuals.
Cost shifting to individuals
Largest impact on safety net hospitals, rural hospitals, children's hospitals, and community health centers
Full impact will not be known for years
To be successful, must start addressing possible solutions now.
Get started with one of the following “NO” responses:
1. No obligation initial consultation - let’s have a brief chat
OR
2. No Thanks, I’ll go it alone