Digital Health Technology Adherence
After reading this article, you will be able to describe the factors influencing poor digital health technology adoption and learn strategies to improve adherence.
SUMMARY:
Digital Health Technologies (DHT) have fostered a new era of personalized health.
Adherence with these devices remains variable.
There are several key factors influencing adherence in either a positive or negative manner.
COMMON PAIN POINTS
No specific model or standardized scale exists to determine DHT adherence reliably.
DHT development is often fragmented, lacks coordination, and consensus on the best practical design.
Studies evaluating DHT adherence do not consistently define the meaning of adherence.
REVIEW
BACKGROUND
DHT includes wearable devices, telemedicine, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence in the delivery of care.
Adherence has been a longstanding challenge within healthcare, and is now an issue with DHT.
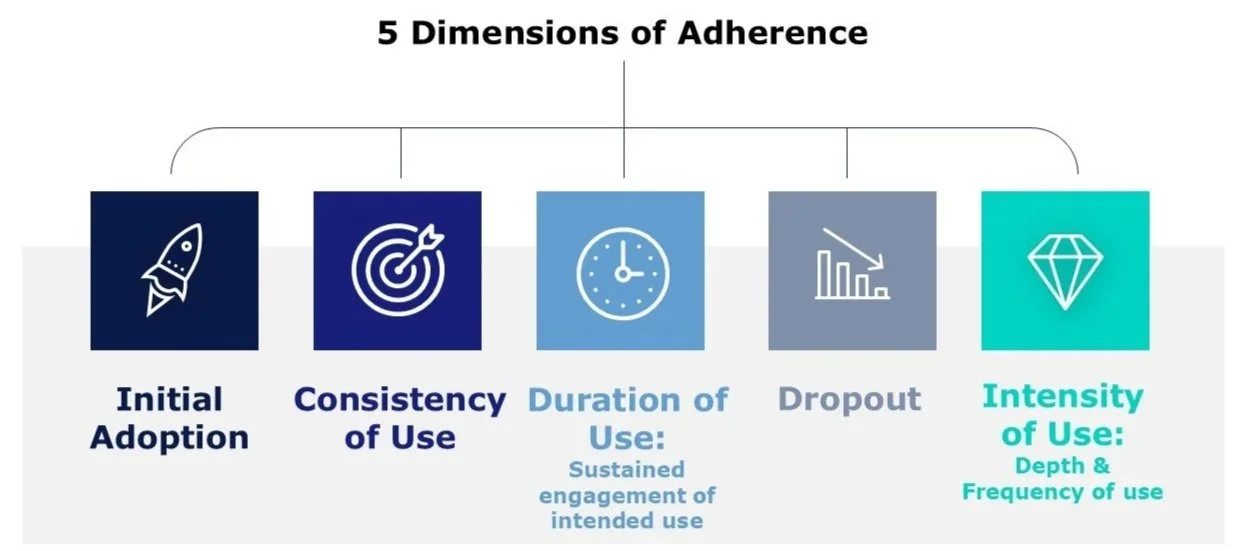
5 DIMENSIONS OF ADHERENCE:
Initial Adoption
Consistency of use
Duration of use (sustained engagement along intended use)
Dropout (discontinuation)
Intensity of use (depth & frequency of use)
Adherence is also categorized as:
Engagement:
How a patient uses and interacts with their DHT
Irrespective of intended use
Directly reflects adherence
Acceptance:
Willingness to use DHT
May predict initial adoption but not sustained adherence
FACTORS INFLUENCING ADHERENCE:
LIMITATIONS:
There is a lack of a standardized scale to reliably predict DHT adherence.
Currently available models were developed for other areas and may not be specific to healthcare.
Current evaluations focus on initial acceptance without assessment of long-term adherence to digital health.
The assessment areas (i.e., engagement, adoption, acceptance, continued use, persistence, drop out) vary in parameters used or are not consistently defined.
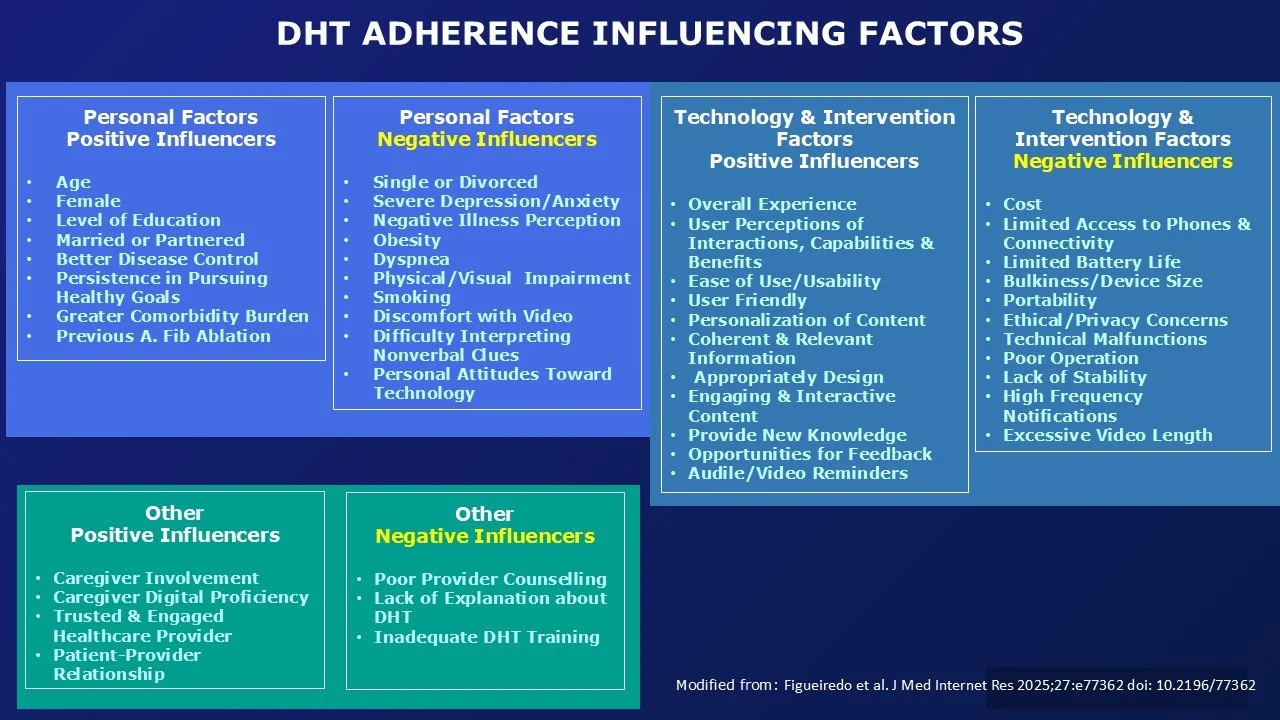
CATEGORIES INFLUENCING DHT ADHERENCE:
Personal Factors:
Demographics:
Age,
Gender,
Education level,
Relationship status,
Employment status.
User Characteristics:
Personal circumstances,
Digital literacy
Health Status:
Comorbidities,
Mental health,
Health condition factors,
Level of disease control,
Smoking status
Personal Beliefs:
Illness perception,
Attitude toward technology
Technology & Intervention Content:
Infrastructure:
Cost of software, application, devices
Limited broadband/cellular coverage
Privacy concerns
Wearables: Bulky, battery life, size
Digital solutions: Portability, durability, storage
User Experience:
User perception of interventions,
Capabilities of device
Overall experience
Benefits of DHT
Ease of use
General usability/friendliness
Technical issues (malfunctions, operation of device, stability of device)
Content & Features
Personalization of the content
Coherent & relevant information
Design features
Engaging/interactive content
Provides new knowledge (not just data)
Direct patient-provider access
Feedback opportunities
Audible/visual reminders
Social & Support Factors:
Family/Caregiver: Supports involvement, especially of those with digital acumen
Patient-Provider Relationship: Level of trust in the provider and the provider's level of engagement
Contextual Factors:
Cultural and Social value: Cultural trust in the healthcare field
Healthcare Provider Influence:
DHT is endorsed by medical guidelines/associations
Previous experience with the DHT
Clear information provided about SHT use
Reimbursement available
STRATEGIES TO DRIVE DHT ADHERENCE:
Develop and implement a system-level perspective for the DHT
DHT development should involve the voice of the patient for enhanced usability, personalization, accessibility, and addressing technical barriers.
Well-defined terms to assess adherence, engagement, acceptance, and dropout rate.
CONCLUSIONS:
DHT provides data, but does not provide insight to patients about the data. Patients do not know how to perceive the value of this information.
Patient involvement from design to interventions is key to building a DHT that patients will adhere to and engage with.
The factors influencing DHT adherence can improve or be a challenge to DHT adherence, and must be considered
Billions are being invested in wearables, remote monitoring, and digital health tools.
Adoption and adherence with these devices are inconsistent.
The problem is not the technology; translating the data into real insight, action, and behavior is the key to success.
A user-centric approach, will enhancing usability, personalization, accessibility, and eliminating technical barriers with co-creation, is the key to success.